即將邁入2019,回顧一下2018 前10名最受喜愛的snap套件是哪些呢?
剛看了一下敝公司的官方網頁,以下有Top10的排行榜唷~ :D
https://blog.ubuntu.com/2018/12/27/top-snaps-in-2018
不過說真的,我個人蠻常用的Skype, mailspring, simplenote現在都用snap來安裝,並且會自動定時更新,超方便的呀~
不知道何時會有line for snap?
Friday, December 28, 2018
Wednesday, September 19, 2018
How can I setup an IPv6 router via radvd on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS?
What's radvd?
Router advertisement daemon.
Reference:
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radvd
http://www.litech.org/radvd/
一般來說 IPv6 Client決定Global IPv6的方式有兩種,分別是Stateless與Stateful,預設radvd是採用stateless IPv6,不過透過更改某個參數(M flag),就可以轉換成stateful,但是此時網路上必須有對應的DHCPv6 server來負責管理與分配IPv6 address。
網路上可以找到很多先進寫的資料關於Stateless與Stateful的差異,我也就不班門弄斧了,廢話不多說,直接進入主題,如何架設radvd在Canonical/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS。
Steps:
Step1. Install radvd package.
以上一個簡單的IPv6 stateless的Router已經架設完成,IPv6 client現在自己可以搭配prefix自動產生host ID。
Router advertisement daemon.
Reference:
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radvd
http://www.litech.org/radvd/
一般來說 IPv6 Client決定Global IPv6的方式有兩種,分別是Stateless與Stateful,預設radvd是採用stateless IPv6,不過透過更改某個參數(M flag),就可以轉換成stateful,但是此時網路上必須有對應的DHCPv6 server來負責管理與分配IPv6 address。
網路上可以找到很多先進寫的資料關於Stateless與Stateful的差異,我也就不班門弄斧了,廢話不多說,直接進入主題,如何架設radvd在Canonical/Ubuntu 18.04 LTS。
Steps:
Step1. Install radvd package.
$ sudo apt-get install radvdStep2. Copy example file of radvid.conf from /usr/share/doc/radvd/examples/ to /etc.
$ sudo cp /usr/share/doc/radvd/examples/radvd.conf.example /etc/radvd.conf
Step3. Open/Edit radvd.conf
根據你的需求,去配置相關的參數,最重要的應該是prefix,更多詳細的參數可以參考man page。
https://www.systutorials.com/docs/linux/man/5-radvd.conf/Step4. Restart radvd
$ sudo systemctl restart radvd; sudo systemctl enable radvd
以上一個簡單的IPv6 stateless的Router已經架設完成,IPv6 client現在自己可以搭配prefix自動產生host ID。
Wednesday, August 15, 2018
How can I configure Ubuntu 16 to start teamviewer automatically?
Steps:
1. Opened /etc/init.d/rc.local
2. Added teamviewer's command and parameter below in file rc.local:
4. Examine if teamviewer daemon can work as expected:
1. Opened /etc/init.d/rc.local
$ sudo vi /etc/init.d/rc.local
2. Added teamviewer's command and parameter below in file rc.local:
teamviewer passwd ubuntu3. Restart system
4. Examine if teamviewer daemon can work as expected:
$ systemctl status teamviewerd
● teamviewerd.service - TeamViewer remote control daemon
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/teamviewerd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since 三 2018-08-15 11:00:14 CST; 1min 25s ago
Process: 1555 ExecStart=/opt/teamviewer/tv_bin/teamviewerd -d (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 1567 (teamviewerd)
CGroup: /system.slice/teamviewerd.service
└─1567 /opt/teamviewer/tv_bin/teamviewerd -d
$ ps aux | grep -i teamviewer
root 1567 0.3 0.3 1181612 12212 ? Sl 11:00 0:00 /opt/teamviewer/tv_bin/teamviewerd -d
u 1890 0.3 2.2 1990224 88556 ? Sl 11:00 0:00 /opt/teamviewer/tv_bin/TeamViewer
Afterwards, you can remote control host via Partner ID and password which is ubuntu in this example.
Friday, May 04, 2018
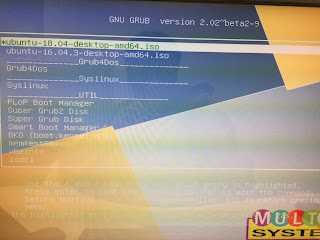
How can I create a multiboot USB stick from Linux?
You can refer to https://www.pendrivelinux.com/multiboot-create-a-multiboot-usb-from-linux/
It works for me!
Above you can see that I am able to boot Ubuntu 16.03 as well as 18.04 with one USB stick w/o problem.
But somehow you've to disable security boot in BIOS.
Enjoy~
It works for me!
Above you can see that I am able to boot Ubuntu 16.03 as well as 18.04 with one USB stick w/o problem.
But somehow you've to disable security boot in BIOS.
Enjoy~
How can I setup a proxy server in Ubuntu 16.04?
Step1. Install package squid
# sudo apt-get install -y squid
Step2. To setup common proxy settings:
# sudo vi /etc/squid/squid.conf
To add some lines below:
# line 977
acl lan src 192.168.1.0/24
(where 192.168.1.0 means network you would like to allow client to access your proxy server)
# line 1189
http_access allow lan
(Allow lan here)
# line 1602
http_port 3128
(To modify default proxy port if needed)
Step3. Restart squid
# sudo systemctl restart squid
Step4. Examine squid service
# sudo systemctl status squid
● squid.service - LSB: Squid HTTP Proxy version 3.x
Loaded: loaded (/etc/init.d/squid; bad; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since 四 2018-04-26 15:24:04 CST; 1min 56s ago
Docs: man:systemd-sysv-generator(8)
Process: 3088 ExecStop=/etc/init.d/squid stop (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 3119 ExecStart=/etc/init.d/squid start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
CGroup: /system.slice/squid.service
├─3159 /usr/sbin/squid -YC -f /etc/squid/squid.conf
├─3161 (squid-1) -YC -f /etc/squid/squid.conf
├─3162 (logfile-daemon) /var/log/squid/access.log
└─3163 (pinger)
四 26 15:24:04 uc16-VirtualBox systemd[1]: Starting LSB: Squid HTTP Proxy version 3.x...
四 26 15:24:04 uc16-VirtualBox squid[3119]: * Starting Squid HTTP Proxy squid
四 26 15:24:04 uc16-VirtualBox squid[3159]: Squid Parent: will start 1 kids
四 26 15:24:04 uc16-VirtualBox squid[3119]: ...done.
四 26 15:24:04 uc16-VirtualBox systemd[1]: Started LSB: Squid HTTP Proxy version 3.x.
四 26 15:24:04 uc16-VirtualBox squid[3159]: Squid Parent: (squid-1) process 3161 started
# netstat -tupln | grep 3128
tcp6 0 0 :::3128 :::* LISTEN 3161/(squid-1)
Done ~
In proxy client side:
You can use tcpdump or wireshark to ensure that http request will go to proxy server after you configured http proxy server within browser.
root@server1:~$ sudo tcpdump -n -v -i any port 3128
tcpdump: listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL (Linux cooked), capture size 262144 bytes
15:29:06.382845 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 2257, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 145)
192.168.1.211.40994 > 192.168.1.254.3128: Flags [P.], cksum 0x85a5 (incorrect -> 0x9ba8), seq 670754847:670754940, ack 314235908, win 237, options [nop,nop,TS val 1731217504 ecr 1884649606], length 93
15:29:06.383195 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 35299, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 212)
192.168.1.254.3128 > 192.168.1.211.40998: Flags [P.], cksum 0xbf6c (correct), seq 2355697405:2355697565, ack 1986317666, win 486, options [nop,nop,TS val 1884649610 ecr 1731217476], length 160
15:29:06.383264 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 17423, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 52)
192.168.1.254.3128 > 192.168.1.211.40994: Flags [.], cksum 0xaba6 (correct), ack 93, win 503, options [nop,nop,TS val 1884649610 ecr 1731217501], length 0
15:29:06.383359 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 2258, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 1353)
192.168.1.211.40994 > 192.168.1.254.3128: Flags [P.], cksum 0x8a5d (incorrect -> 0x8fe0), seq 93:1394, ack 1, win 237, options [nop,nop,TS val 1731217505 ecr 1884649610], length 1301
15:29:06.384198 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 9911, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 268)
Wednesday, April 11, 2018
How can I setup a Linux NAT Router in Ubuntu?
Steps:
1. Enable packet forwarding for IPv4 between NICs:
Done~
1. Enable packet forwarding for IPv4 between NICs:
- Open and edit /etc/sysctl.conf
- Ucomment net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
- To execute command sysctl -p
- iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o enp0s8 -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j MASQUERADE
- Where enp0s8 is WAN and 192.168.1.0/24 is LAN, please modify those parameters depend on your environment.
- Save rules: iptables-save > /etc/iptables.save
- Restore rules:
- Open and edit /etc/network/interfaces to add pre-up.....
# interfaces(5) file used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8)
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto enp0s3
iface enp0s3 inet static
address 192.168.1.254
netmask 255.255.255.0
pre-up iptables-restore < /etc/iptables.save
Done~
Tuesday, February 27, 2018
如何在Ubuntu 16.04 desktop 透過PXE安裝Ubuntu?
在開始之前,請先準備與安裝相關的service在Ubuntu desktop 16.04 LTS:
準備:
1. Download Ubuntu desktop ISO
2. Download PXE bootloader
安裝:
1. DHCP Server
1. DHCP Server:
* 補充: 針對18.04要修改一下設定檔如下:
APPEND initrd=./u18/initrd_ubuntu18.04.lz root=/dev/nfs boot=casper netboot=nfs nfsroot=192.168.1.254:/var/nfs/ubuntu18.04 splash toram --
4. NFS file Server:
Boot from Network boot:
Done!
準備:
1. Download Ubuntu desktop ISO
2. Download PXE bootloader
安裝:
1. DHCP Server
$ sudo apt-get install isc-dhcp-server2. TFTP Server
$ sudo apt-get install tftpd-hpa inetutils-inetd3. NFS Server
$ sudo apt-get install nfs-kernel-server配置:
1. DHCP Server:
$ sudo vi /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
subnet 192.168.1.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 192.168.1.200 192.168.1.253;
option domain-name-servers 8.8.8.8;
option routers 192.168.1.1;
option broadcast-address 192.168.1.255;
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
next-server 192.168.1.254;
filename "pxelinux.0";
}
$ sudo systemctl restart isc-dhcp-server2. TFTP Server:
$ sudo vi /etc/default/tftpd-hpa
TFTP_USERNAME="tftp"
TFTP_DIRECTORY="/var/lib/tftpboot"TFTP_ADDRESS=":69"
TFTP_OPTIONS="--secure"
RUN_DAEMON="yes"
OPTIONS="-l -s /var/lib/tftpboot"
$ sudo vi /etc/xinetd.conf
tftp dgram udp wait root /usr/sbin/in.tftpd /usr/sbin/in.tftpd -s /var/lib/tftpboot
$ sudo systemctl restart tftpd-hpa3. PXE bootloader:
$ tar -xJf syslinux-6.03.tar.xz
$ cd syslinux-6.03
$ sudo cp bios/core/pxelinux.0 /var/lib/tftpboot
$ sudo cp bios/com32/lib/libcom32.c32 /var/lib/tftpboot
$ sudo cp bios/com32/libutil/libutil.c32 /var/lib/tftpboot
$ sudo cp bios/com32/elflink/ldlinux/ldlinux.c32 /var/lib/tftpboot
$ sudo cp bios/com32/menu/vesamenu.c32 /var/lib/tftpboot
$ mkdir /var/lib/tftpboot/pxelinux.cfg
$ sudo vi /var/lib/tftpboot/
pxelinux.cfg/default
DEFAULT vesamenu.c32* Remember to copy vmlinuz.efi and initrd.lz to the folder /var/lib/tftpboot from Ubuntu ISO.
MENU TITLE Network boot
LABEL ubuntu-mate-16.04.2-desktop-amd64
MENU LABEL ubuntu-mate-16.04.2-desktop-amd64
KERNEL vmlinuz.efi
APPEND initrd=initrd.lz root=/dev/nfs boot=casper netboot=nfs nfsroot=192.168.1.254:/var/nfs/ubuntu_desktop splash --
* 補充: 針對18.04要修改一下設定檔如下:
APPEND initrd=./u18/initrd_ubuntu18.04.lz root=/dev/nfs boot=casper netboot=nfs nfsroot=192.168.1.254:/var/nfs/ubuntu18.04 splash toram --
4. NFS file Server:
$ sudo mount -o loop ubuntu-16.04.3-desktop-amd64.iso /mnt/
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/nfs/ubuntu_desktop
$ sudo cp -rf /mnt/* /var/nfs/ubuntu_desktop/
$ sudo vi /etc/exports
/var/nfs/ubuntu_desktop *(ro,sync)
$ sudo systemctl restart nfs-kernel-server
$ showmount -e localhost
Export list for localhost:
/var/nfs/ubuntu_desktop *
Boot from Network boot:
Done!
Tuesday, February 13, 2018
How can I move Launcher from left to the buttom on Ubuntu 16.04?
It's very simple, and it works for me even if I reboot or re-login the system b/c Ubuntu will remember it.
Steps:
1. Open a terminal
2. To execute "gsettings set com.canonical.Unity.Launcher launcher-position Bottom"
Done~
Steps:
1. Open a terminal
2. To execute "gsettings set com.canonical.Unity.Launcher launcher-position Bottom"
Done~
Sunday, February 04, 2018
How can I get detail information of USB device?
The command lsusb, which able to list all USB devices of machine below:
However, I would like to know more informations. For example, speed, vendor, manufacturer......, etc. And there is a command usb-devices, which can help me.
Above you can see the Spd=480/USB 2.0, and Spd=5000/USB 3.0.
lawrence@Lawrence-ThinkPad-X200:~$ lsusb
Bus 002 Device 004: ID 7392:7711 Edimax Technology Co., Ltd EW-7711UTn nLite Wireless Adapter [Ralink RT2870]
Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
Bus 008 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
Bus 007 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
Bus 006 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
Bus 001 Device 003: ID 17ef:480c Lenovo Integrated Webcam
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub
Bus 005 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
Bus 004 Device 002: ID 08ff:2810 AuthenTec, Inc. AES2810
Bus 004 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
Bus 003 Device 001: ID 1d6b:0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
lawrence@Lawrence-ThinkPad-X200:~$ usb-devices
T: Bus=02 Lev=01 Prnt=01 Port=00 Cnt=01 Dev#= 4 Spd=480 MxCh= 0
D: Ver= 2.00 Cls=00(>ifc ) Sub=00 Prot=00 MxPS=64 #Cfgs= 1
P: Vendor=7392 ProdID=7711 Rev=01.01
S: Manufacturer=RalinkS: Product=802.11 n WLAN
S: SerialNumber=1.0
C: #Ifs= 1 Cfg#= 1 Atr=80 MxPwr=450mA
I: If#= 0 Alt= 0 #EPs= 7 Cls=ff(vend.) Sub=ff Prot=ff Driver=rt2800usb
T: Bus=04 Lev=00 Prnt=00 Port=00 Cnt=00 Dev#= 1 Spd=5000 MxCh= 2
D: Ver= 3.00 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=03 MxPS= 9 #Cfgs= 1
P: Vendor=1d6b ProdID=0003 Rev=04.13
S: Manufacturer=Linux 4.13.0-32-generic xhci-hcd
S: Product=xHCI Host Controller
S: SerialNumber=0000:0d:00.0
C: #Ifs= 1 Cfg#= 1 Atr=e0 MxPwr=0mA
I: If#= 0 Alt= 0 #EPs= 1 Cls=09(hub ) Sub=00 Prot=00 Driver=hub
Above you can see the Spd=480/USB 2.0, and Spd=5000/USB 3.0.
Sunday, January 28, 2018
[Shell script] Find user in system
#!/bin/bash
if [ $# -eq 0 ]
then
echo "Usage: $0 lawrence"
else
grep "\<$1\>" /etc/passwd > /dev/null
RETVAL=$?
if [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ]
then
echo "Username $1 was found in the system"
else
echo "Cannot find username $1"
fi
fi
The second way:
[ $# -eq 0 ] && { echo "Usage: $0 lawrence" ; exit 1; }
grep "\<$1\>" /etc/passwd > /dev/null
RETVAL=$?
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && echo "Username $1 was found in the system" || echo "Cannot find username $1"
Thursday, January 04, 2018
How can I add EPEL reop on CentOS 7.x?
It's quite simple, just two commands below:
# yum install epel-release
# yum repolist
Sample output:
# yum install epel-release
# yum repolist
Sample output:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)